树的遍历方式
- 前序遍历: 根节点->左子树->右子树
- 中序遍历: 左子树->根节点->右子树
- 后序遍历: 左子树->右子树->根节点
例如下面二叉树的三种遍历
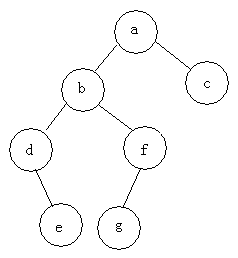
- 前序遍历:abdefgc
- 中序遍历:debgfac
- 后序遍历:edgfbca
每种遍历都有递归跟循环两种实现方式,每一种遍历的递归实现都比循环实现简捷很多。
还有一种遍历方式
代码实现
树节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| //树节点
private class BinaryTreeNode{
String data;
BinaryTreeNode leftChild;
BinaryTreeNode rightChild;
public BinaryTreeNode(String data,BinaryTreeNode leftChild,BinaryTreeNode righjtChild){
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = righjtChild;
}
public BinaryTreeNode(String data){
this(data,null,null);
}
}
|
前序遍历
递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| //前序遍历递归实现
public void preOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
System.out.println(node.data);
preOrder(node.leftChild);
preOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
|
非递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public void nonRePreOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(node);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
node = stack.pop();
System.out.println(node.data);
if(node.rightChild!=null)
stack.push(node.rightChild);
if(node.leftChild!=null)
stack.push(node.leftChild);
}
}
}
|
中序遍历
递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public void inOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
inOrder(node.leftChild);
System.out.println(node.data);
inOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
|
非递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public void nonReInOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
BinaryTreeNode p = node;
while(p!=null||stack.size()>0){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.leftChild;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
p=stack.pop();
System.out.println(p.data);
p=p.rightChild;
}
}
}
|
后序遍历
递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public void postOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
postOrder(node.leftChild);
postOrder(node.rightChild);
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
|
非递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public void nonRePostOrder(BinaryTreeNode p){
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
BinaryTreeNode node = p;
while(p!=null){
//左子树入栈
for(;p.leftChild!=null;p=p.leftChild){
stack.push(p);
}
//没有右子树或者右子树已经被处理了
while(p!=null&&((p.rightChild==null)||(p.rightChild==node))){
myprint(p.data);
node=p;
if(stack.isEmpty())
return;
p=stack.pop();
}
//处理右子树
stack.push(p);
p=p.rightChild;
}
}
|
层序遍历
非递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public void nonRelevelOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node==null)
return;
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BinaryTreeNode nodeTmp = queue.poll();
System.out.println(nodeTmp.data);
if(nodeTmp.leftChild!=null)
queue.add(nodeTmp.leftChild);
if(nodeTmp.rightChild!=null)
queue.add(nodeTmp.rightChild);
}
}
|
特殊场景,只打印某层的节点
没有返回值,直接打印
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| //只打印二叉树某层的节点,第一层是0层
public boolean printNodeAtLevelOne(BinaryTreeNode root,int level){
if(root==null||level<0)
return false;
if(level==0){
myprint(root.data+"");
return true;
}
boolean left = printNodeAtLevelOne(root.leftChild,level-1);
boolean right = printNodeAtLevelOne(root.rightChild,level-1);
return left||right;
}
|
将值放在List中返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| //只打印二叉树某层的节点,第一层是0层,节点值存储在list中
public boolean printNodeAtLevelTwo(BinaryTreeNode root, int level, List<String> list) {
if (root == null || level < 0) {
return false;
}
if (level == 0) {
list.add(root.data);
return true;
}
boolean left = printNodeAtLevelTwo(root.leftChild, level-1, list);
boolean right = printNodeAtLevelTwo(root.rightChild, level-1, list);
return left || right;
}
|
备忘
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public void printNodeAtLevelSelf(BinaryTreeNode root,int level){
if(root==null||level<0)
return ;
if(level==0){
myprint(root.data+"");
return ;
}
printNodeAtLevelSelf(root.leftChild,level-1);
printNodeAtLevelSelf(root.rightChild,level-1);
}
|
递归实现(无返回值)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public void levelOrderOne(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return ;
for(int level = 0; ; level++) {
if (!printNodeAtLevelOne(root, level))
break;
}
}
|
递归实现(有返回值)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| //树的层序遍历 见编程之美 分层遍历二叉树
public List<List<String>> levelOrderTwo(BinaryTreeNode root) {
List<List<String>> lists = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
if (root == null)
return lists;
for (int level = 0; ; level++) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (!printNodeAtLevelTwo(root, level, list))
break;
lists.add(0, list);
}
return lists;
}
|
几种场景
前序遍历 用深度标记节点
中序遍历 顺序打印搜索二叉树的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public void inOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
inOrder(node.leftChild);
myprint(node.data);
inOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
|
后序遍历 求节点的高度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public int height(BinaryTreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return -1;
else
return 1+Math.max(height(root.leftChild),height(root.rightChild));
}
|
上一篇:AsyncTask的基本用法


